Docker
Docker is a platform designed to create, deploy, and run applications using host OS memory in isolated packages of code called containers. That means every application running on docker is fully isolated from other docker applications. Docker usage Container on top of host OS to run the applications to achieve isolation. This is called Containerized Application.
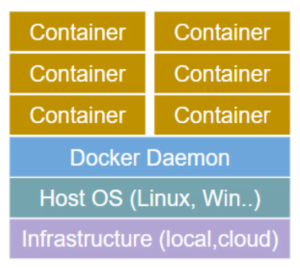
Docker Daemon is the background process that manages Docker objects such as images, containers, networks, and volumes.
Dockerfile
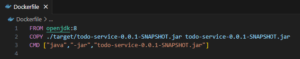
Dockerfile is a simple text file that consists of instructions to build Docker images.
For example – we want to create a Docker image based on a build Java Todo Application in your local machine.
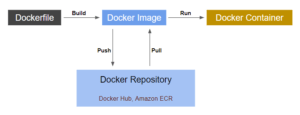
Docker Image
Docker Image is the executable package of a software that includes everything needed to run the application. Above Todo Application is a complete Docker image. You just need to pull the image by docker command from Docker Registry (Docker Hub) and run as many times as you need in your device (local, cloud).
Where do we find/store docker images ?
- Docker Hub (Public repo)
- Amazon ECR (Elastic Container Registry) (Public and Private repo)
Docker Container
Docker Container is the running instance of a Docker Image. This is the environment where the application runs isolated from the host system and other containers.
Docker Volume
Let’s say a container is running with MySQL but It needs to be removed anyway and run another again then all data will be lost. Database is not a thing you want to lose. In this case we need persistent data for Docker applications and Docker Volume comes in the picture.
Volumes allow you to persist data generated by containers and share data between containers.
Docker Networking
Without networking someone’s cool features are never recognized to the outside world. Same for Docker. Docker Networking allows us to expose the containers (Applications) to external networks and other containers to communicate.





0 Comments